Solutions to Water Scarcity based on Machine Learning
Abstract
This paper uses various methods including population forecasting, neural networks, and regression analysis to address water scarcity in North China. It establishes water demand and supply models, highlighting social and environmental drivers of scarcity. The study calculates a water gap of 35.8 billion cubic meters and explores intervention strategies like building reservoirs and water transfer projects. It also analyzes pollution and sewage disposal, discussing the plan's strengths, weaknesses, and impacts on the ecosystem.
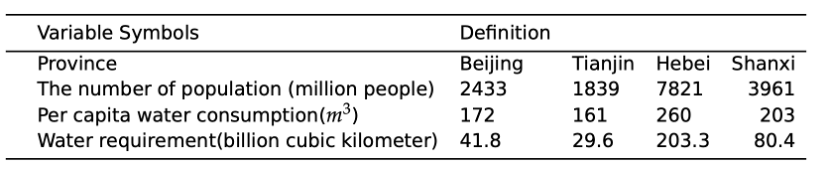
The forecast of water demand using population prediction model
To anticipate future water needs in a region, a dynamic model is essential. By predicting water demand for the next 15 years based on population growth, we calculate the gap between supply and demand. Assuming constant per capita usage without large-scale conservation efforts, this usage depends on provincial populations. Using the Logistic population forecast model for 2030, we estimate water needs considering available resources. The Logistic function model is utilized for this prediction.
This table shows the Water requirement of all provinces in North China in 2030:
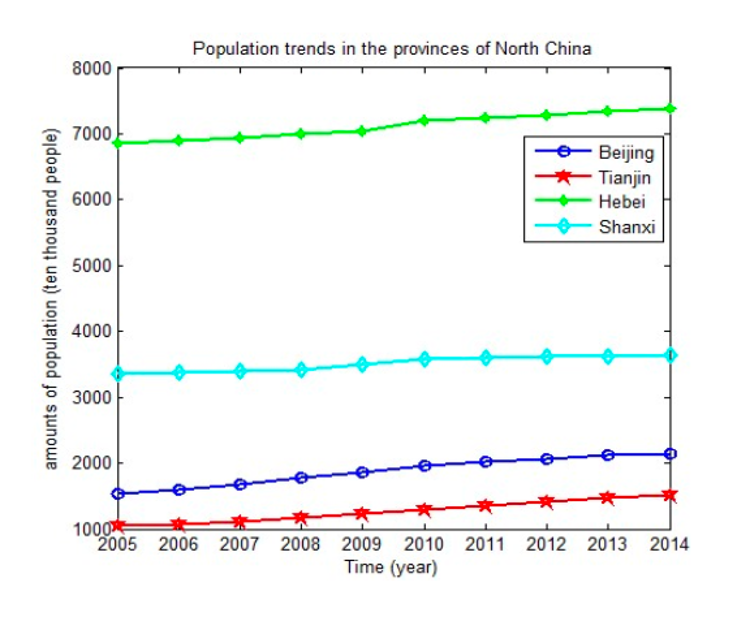
The prediction model of water supply based on GM(1,1)
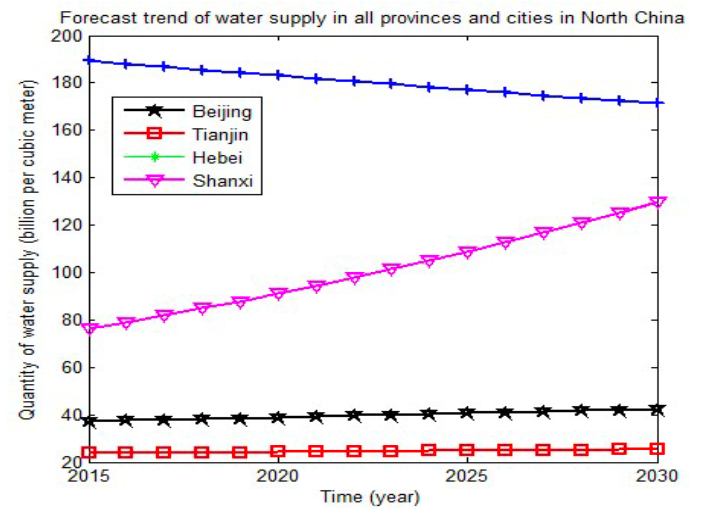
In order to get the gap in water resources in 2030, supply quantities of various provinces and cities in North China are predicted in this paper by the establishment of the grey prediction model GM(1,1). The results as shown in the following figure:
The table shows the final predicted value of water supply in various provinces in 2030:

At the same time, it can be seen from the figure above that the water supply in Hebei province has a clear downward trend, which is caused by the development of industrial water pollution and the imperfect water resources management system. Shanxi has a slight rise, which is prone to drought, the rise of this year’s water supply is contributed by the implementation of the Huang Jijin project. There is no change in Tianjin and Beijing. Basically, the amount of water supply in the North China area is of a certain stable range and will be sustainably supplied in the near future. But it is known by the situation of population and demand, that the water resources will be unable to meet the needs of production and daily life with the increase of population and rising demand for water. If the water supply remains the same as the original level and the law of development, without any measures, the situation will be more and more severe. The resulting gap is shown in the figure:
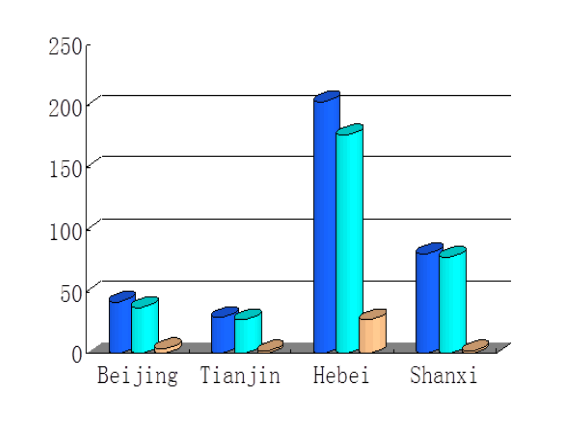
As is shown in figures above, the total amount of water gap in North China is 35.8 billion cubic meters, if there is no effective strategy water resources program, Hebei will face a great shortage of water resources by 2030. Beijing, Tianjin, and Shanxi will also face varying degrees of water shortage soon. The shortage of water resources will restrict the development of industrial and agricultural production in North China, and affect the normal production and life of people.
Testing on the model
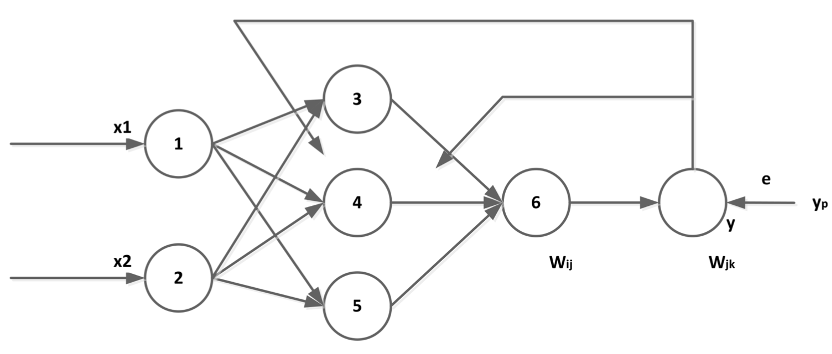
The BP (Back Propagation) Neural Network involves a learning process using the error back-propagation algorithm. It includes forward propagation, where input information is transferred through input and middle layers, which can be Single Hidden Layer or Multiple Hidden Layer structures. The output is generated through the output layer. If there's a difference between expected and actual output, the error triggers backpropagation. This adjusts weights in all layers until an accepted error or the preset learning time is achieved. We designed a Neural Network which is shown as follows:
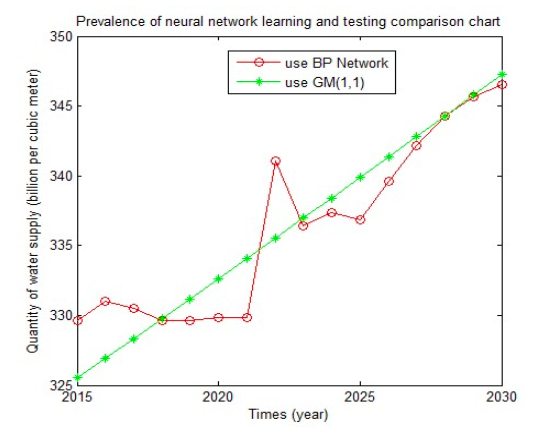
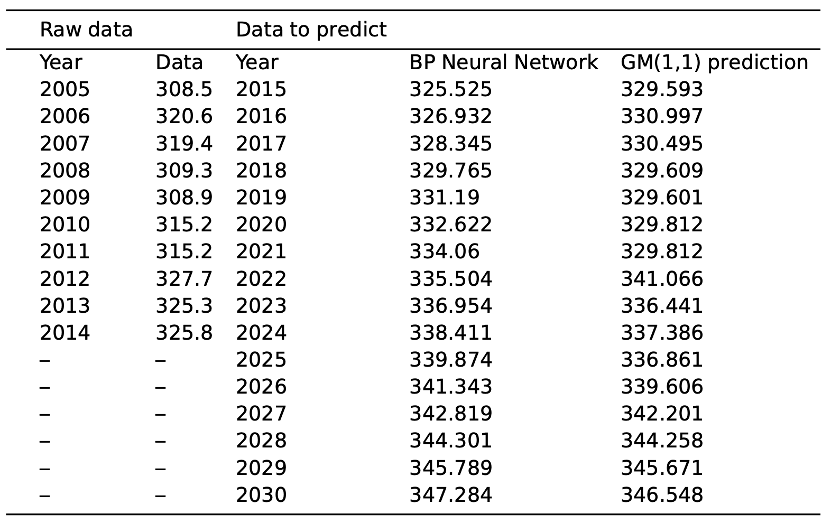
To outburst the difference and efficiency, we transform the official data to the actual number of people who have been infected every week. And test the prediction error and precision of GM (1,1) using BP Neural Network and the Gray prediction. The results are as follows:
The problem analysis with an intervention plan
Intervention plan 1: Building reservoirs
First of all, we determine the number of reservoirs that should be built on the supply and demand of various provinces water supply and demand. Then evaluate of the effectiveness of the construction of the reservoirs through the impact of their flood control, power generation, aquaculture, and other aspects. The following table can be gathered by looking at the reservoirs’ capacity and quantity in provinces and cities. And from that table, it can be seen that the area reservoir capacity in each area is not identical, it is related to different geographical factors and development strategies.

According to the average reservoir capacity, the number and capacity of the reservoir should be built in each province, that is, The quantity and capacity of the reservoirs will be built in various provinces as Tab.6, based on the average reservoir capacity.

Intervention plan 2: South-to-North Water Diversion Project
Through the study on the storage of water resources we can find that, though certain ecological benefits and economic benefits similar to electric power are contributed by the reservoirs, a big problem is that the sustainability is poor for a reservoir is available just for 50 years. Thus the flow problem of water resources will be discussed in this section, making up the shortcomings of reservoirs based on existing desalination plants and Water Transfer Projects. Generally there are many flow manners of water resources, of those, the transfer project has a good advantage to provide water resources effectively and efficiently, like desalination plants and Water Transfer Projects.
Intervention plan 3: Desalination plants
Desalination plant is an important field to explore actively. Getting fresh water from the ocean, this worldwide issue has become a burgeoning industry. According to the current situation of China’s technology development, the desalination cost is between 4 and 7 yuan per square meter. Most importantly, with the possible application of new technologies such as steam distillation, dew point evaporation, the desalination cost will continue to decline in the future.
Intervention plan 4: Water resources protection and sewage treatment
Environmental pollution, including the problems which lead to the production of sewage, water shortages, and other serious impact on the quality of water resources. It makes sewage discharge and treatment very important, so we need to ease the water shortage problem by the means of building a sewage treatment plant. The value of the objective function is greater, the more serious the pollution in the area, the need to establish a sewage treatment plant is greater. We can calculate the values of each of the provinces and observe the pollution degree by using the prediction of the population above, forecast of the sewage emissions and sewage ammonia nitrogen, in order to provide the basis for the necessity to build a sewage treatment plant. The constant value of ammonia nitrogen content in the units of various provinces and cities is shown in this table:

The regression analysis is made to predict the total wastewater in 2030 in the total discharge of sewage of the provinces in North China. Take Hebei Province as an example, and draw the scatterplot and curve fitting. The results are shown in the following figure:
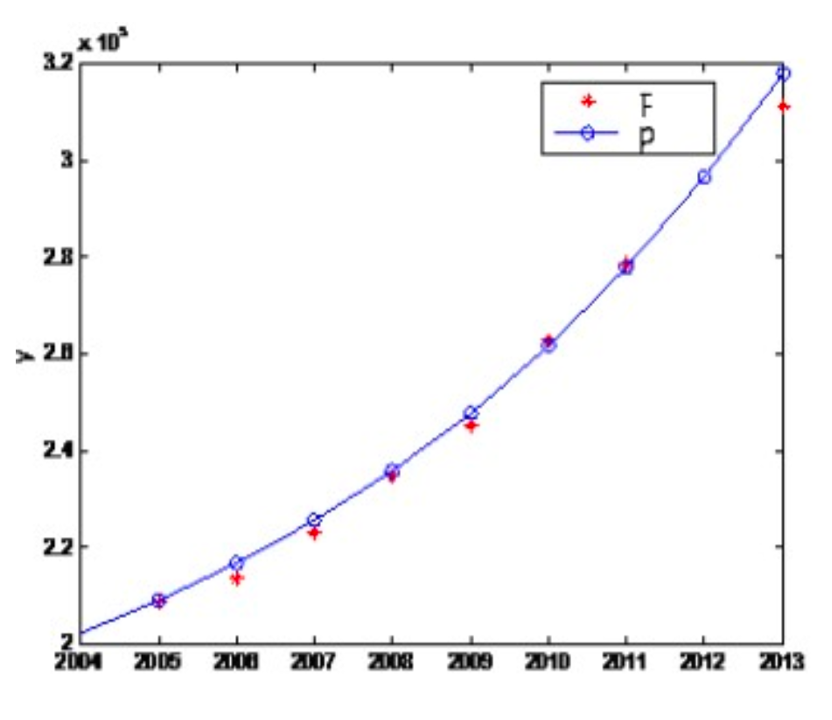
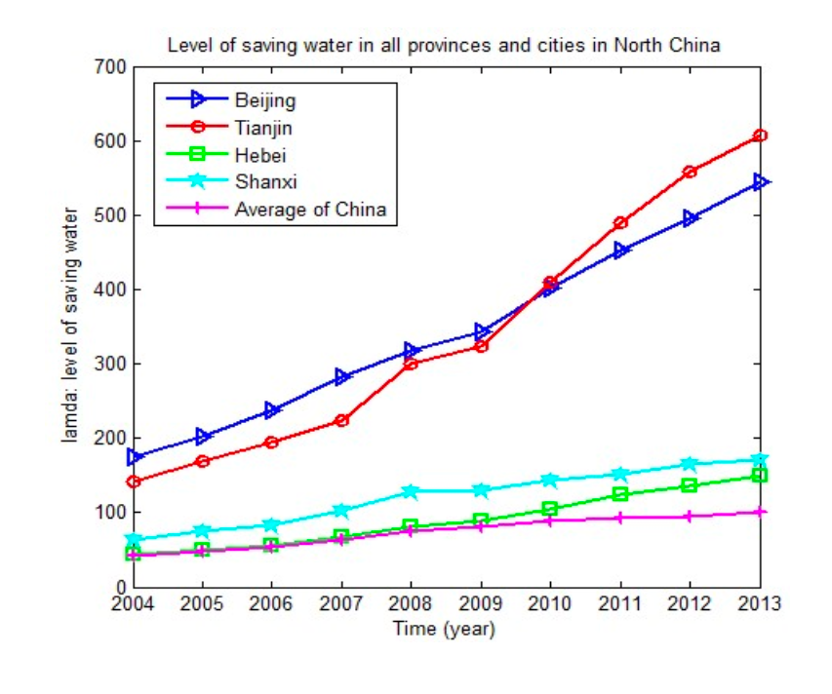
From the figure, it can be seen that the total discharge of sewage is year by year-index rising trend in Hebei Province from 2004 to 2013. That means with the development of social economy and population, industrialization deepens and living wastewater increases. As a result, sewage emissions continue to increase, great influence is caused on the environment, and the wastewater treatment needs are increasing.